Reverse Proxy
Overview
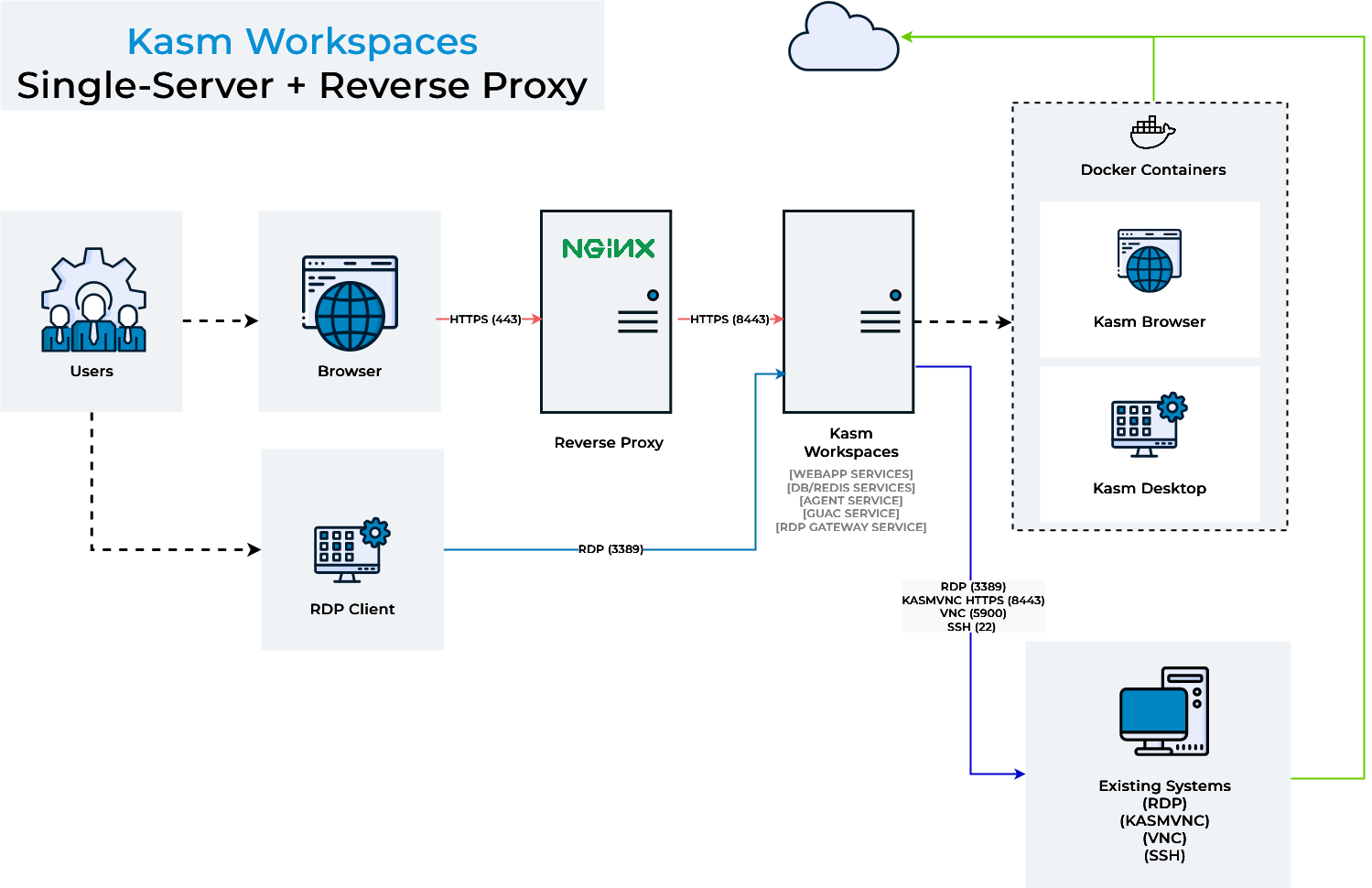
Administrators may desire to run Kasm Workspaces behind a reverse proxy such as Nginx or Caddy . A handful of configurations are required for communication to properly flow between the proxy and Kasm.
Once Kasm is placed behind a reverse proxy, be sure to update the Zone configuration. See Update Zones.
Troubleshooting info can be found on the Troubleshooting Page
Running Kasm Workspaces on a Non-Standard Port
By default, Kasm Workspaces will listen on port 443. Administrators may wish to run the application on another port so that the reverse proxy can run on port 443.
During the installation pass the -L flag to choose a different port.
e.g sudo bash kasm_release/install.sh -L 8443
Users will now access Kasm Workspaces via the defined port https://kasm.server:8443
Example Nginx Config
Below is an example Nginx config with the appropriate settings for Kasm annotated. In this example, Nginx is listening on port 443 and Kasm Workspaces is listening on port 8443
server {
listen 443 ssl;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
location / {
# The following configurations must be configured when proxying to Kasm Workspaces
# WebSocket Support
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
# Host and X headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Should match the listening port of this proxy
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port 443;
# Connectivity Options
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_read_timeout 1800s;
proxy_send_timeout 1800s;
proxy_connect_timeout 1800s;
proxy_buffering off;
# Allow large requests to support file uploads to sessions
client_max_body_size 10M;
# Proxy to Kasm Workspaces running locally on 8443 using ssl
proxy_pass https://127.0.0.1:8443 ;
}
}
Multiple Server Names
Kasm supports proxying via subdomains (e.g https://kasm1.example.com/ / https://kasm2.example.com/) or paths (e.g https://example.com/kasm1/ / https://example.com/kasm2/)
Proxy via Subdomain
Use a dedicated server_name for traffic destined for Kasm. (e.g https://kasm.example.com/). See
Nginx Server Names documentation for more details.
Example Nginx Config
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name app1.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
location / {
return 200 'App 1';
add_header Content-Type text/plain;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name kasm.example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
location / {
# The following configurations must be configured when proxying to Kasm Workspaces
# WebSocket Support
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
# Host and X headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Should match the listening port of this proxy
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port 443;
# Connectivity Options
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_read_timeout 1800s;
proxy_send_timeout 1800s;
proxy_connect_timeout 1800s;
proxy_buffering off;
# Allow large requests to support file uploads to sessions
client_max_body_size 10M;
# Proxy to Kasm Workspaces running locally on 8443 using ssl
proxy_pass https://127.0.0.1:8443 ;
}
}
Example Caddy Config
Below is an example Caddy v2 config with the appropriate settings for Kasm. In this example, Caddy is configured to listen for requests on kasm.example.com and reverse proxy them to Kasm running on https://127.0.0.1:8443 Note that we include the tls_insecure_skip_verify option to skip TLS certificate verification. For more information on configuring Caddy, check out the Caddy documentation at https://caddyserver.comcaddyfile/directives/reverse_proxy#defaults
kasm.example.com {
reverse_proxy https://127.0.0.1:8443 {
transport http {
tls_insecure_skip_verify
}
# Should match the listening port of this proxy
header_up X-Forwarded-Port "443"
}
}
Example HAProxy Config
Below is an example HAProxy config with the appropriate settings for Kasm annotated. In this example HAProxy is listening on port 443 and Kasm Workspaces is listening on port 8443
global
log /dev/log local0
log /dev/log local1 notice
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
stats socket /run/haproxy/admin.sock mode 660 level admin expose-fd listeners
stats timeout 30s
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
# Default SSL material locations
ca-base /etc/ssl/certs
crt-base /etc/ssl/private
ssl-default-bind-ciphers ECDH+AESGCM:DH+AESGCM:ECDH+AES256:DH+AES256:ECDH+AES128:DH+AES:RSA+AESGCM:RSA+AES:!aNULL:!MD5:!DSS
ssl-default-bind-options no-sslv3
defaults
log global
mode http
option httplog
option dontlognull
timeout connect 5000
timeout client 50000
timeout server 50000
errorfile 400 /etc/haproxy/errors/400.http
errorfile 403 /etc/haproxy/errors/403.http
errorfile 408 /etc/haproxy/errors/408.http
errorfile 500 /etc/haproxy/errors/500.http
errorfile 502 /etc/haproxy/errors/502.http
errorfile 503 /etc/haproxy/errors/503.http
errorfile 504 /etc/haproxy/errors/504.http
frontend localhost
bind *:443 ssl crt /tmp/all.pem alpn http/1.1
redirect scheme https if !{ ssl_fc }
mode http
default_backend node
backend node
mode http
option forwardfor
server kasm 127.0.0.1:8443 check ssl verify none
http-request set-header X-Forwarded-Port %[dst_port]
http-request add-header X-Forwarded-Proto https if { ssl_fc }
Example Apache Config
Below is an example Apache config with the appropriate settings for Kasm annotated. In this example, Apache is listening on port 443 and Kasm Workspaces is listening on port 8443.
<VirtualHost *:443>
# Server and ssl
ServerName kasm.example.com
SSLEngine on
SSLCertificateFile /etc/ssl/apache2/server.pem
SSLCertificateKeyFile /etc/ssl/apache2/server.key
# Websocket upgrade
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond ${HTTP:Upgrade} websocket [NC]
RewriteCond ${HTTP:Connection} upgrade [NC]
RewriteRule .* "wss://127.0.0.1:8443/$1" [P,L]
# Proxy
SSLProxyEngine on
SSLProxyVerify none
SSLProxyCheckPeerCN off
SSLProxyCheckPeerName off
SSLProxyCheckPeerExpire off
ProxyPreserveHost on
ProxyPass / https://127.0.0.1:8443/
ProxyPassReverse / https://127.0.0.1:8443/
ProxyRequests off
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Proto https
# Should match the listening port of this proxy
RequestHeader set X-Forwarded-Port 443
</VirtualHost>
Proxy via Path
The same settings need to be sent as with subdomain proxies, we are sending the majority outside of the location block so that they apply to all the locations, but feel free to change this to suit your needs.
Set Proxy Path global setting
- Select Settings > Global from the navigation menu.
- Find the Proxy Path setting and update the value to match the path for this server. The value should start with a trailing slash, therefore if the path url in the address bar looks like
https://example.com/kasm1/#/settingsthen the value entered should be /kasm1
Do not use paths that overlap, for example /kasm and /kasm2 as it will cause issues. This is only the case for where it's an exact overlap from the beginning including the slash. /kasm and /mykasm would be fine, /server and /servers-us would not be. When setting up for the first time, on initial login a cookie will be set for the root / location. After setting a path value and logging out and logging in again, the correct cookie will be set, but the original root cookie will also still exist. It is recommended to clear cookies before logging in to prevent any conflicts when first setting up.
Example Nginx Config
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name example.com;
ssl_certificate /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.crt;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/nginx/ssl/nginx.key;
# The following configurations must be configured when proxying to Kasm Workspaces
# WebSocket Support
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
# Host and X headers
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Proto $scheme;
# Should match the listening port of this proxy
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-Port 443;
# Connectivity Options
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_read_timeout 1800s;
proxy_send_timeout 1800s;
proxy_connect_timeout 1800s;
proxy_buffering off;
# Allow large requests to support file uploads to sessions
client_max_body_size 10M;
location /kasm1/ {
# Proxy to Kasm Workspaces running locally on 8443 using ssl
proxy_pass https://127.0.0.1:8443/;
}
location /kasm2/ {
# Proxy to Kasm Workspaces running externally over ssl
proxy_pass https://kasm.example.com/;
}
}
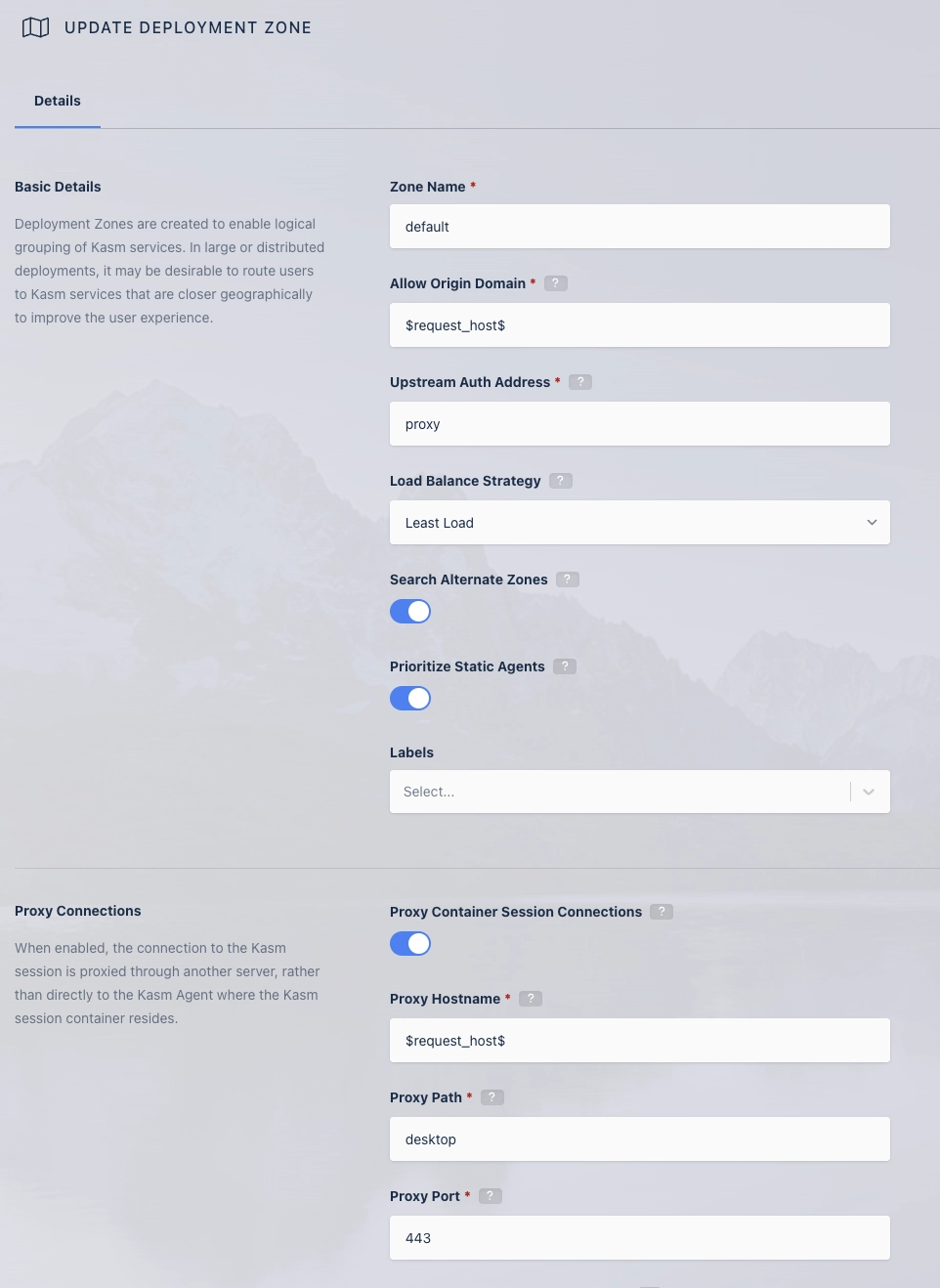
Update Zones
In order for clients to properly make connections to Kasm sessions when using a reverse proxy, the Upstream Auth Address and Proxy Port settings for each [deployment zone](../glossary#deployment zone) must be updated. Update the Proxy Port setting to 0, and Kasm Workspaces will attempt to automatically determine the correct port from window.location.port. Update the Upstream Auth Address with either the word "proxy" or the IP or FQDN of the Kasm Workspaces server if using a single-server installation or if using a multi-server deployment, using the IP or FQDN of the Web App role for that Zone.
Updates to Zone settings are applied to new sessions created after the change. Resuming existing sessions will not have the changes applied.
- Log into the Kasm Workspaces UI as an administrator.
- Select Infrastructure -> Zones.
- Edit the default Zone.
- Change the Upstream Auth Address setting to the "proxy" or the IP or FQDN of the Kasm Workspaces server. If using reverse proxy via path then it needs to be the IP or FQDN that points directly to the upstream server if using a multiserver setup.
- Change the Proxy Port setting to 0.
- Repeat for each additional Zone.
If you are using the RDP local client workspace option, make sure the Restrict RDP Client IP Address setting is disabled in Infrastructure / Zones. If it isn't may not be able to connect, as the IP stored with the request will differ due to the connection being over a reverse proxy. If this is the case it will be reported in the Error Logs with a message such as "Invalid Request. Wrong client IP."